Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes of North America, is an awe-inspiring and majestic body of water that stretches across the international border between the United States and Canada. With its vastness and depth, Lake Ontario holds within its depths a treasure trove of wonders waiting to be explored. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on a captivating journey to unveil the secrets and mysteries beneath this magnificent lake’s surface.
Overview of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is the smallest in surface area among the Great Lakes, but it exceeds Lake Erie in volume. It is located in the easternmost part of the Great Lakes and is the 13th largest lake in the world, with a shoreline of 712 miles. The lake has an elevation of 246 feet above sea level and an average depth of 283 feet, with a maximum depth of 802 feet. The primary inlet of the lake is the Niagara River, and the primary outlet is the St. Lawrence River. The lake is home to several notable geographic features, including Hamilton Harbour, the Bay of Quinte, the Toronto Islands, and the Thousand Islands.
The lake serves as a major fruit-growing and wine-making area, and the Canadian part of the south shore, known as the Niagara Peninsula, is a significant fruit-growing area. With the exception of Rochester, New York, and the considerably smaller port of Oswego, New York, the American coast of the lake is primarily rural. The lake is accessible through several waterways, including the Great Lakes Waterway, the Trent-Severn Waterway, and the Rideau Waterway. The lake’s watershed is home to approximately nine million people, which accounts for over a quarter of Canada’s population.

Depth and Volume
The Depth of Lake Ontario: Lake Ontario is renowned for its remarkable depth, making it one of the deepest lakes in the world. Its maximum depth reaches an astounding 244 meters (800 feet), equivalent to approximately 80 stories in a skyscraper. This staggering depth contributes to the lake’s allure and serves as a testament to its natural grandeur.
When it comes to the volume of water contained within its basin, Lake Ontario holds an extraordinary amount. Its vast volume is estimated to be around 1,639 cubic kilometers (393 cubic miles), providing a sense of the immense scale of this majestic water body. To put it into perspective, Lake Ontario’s volume is equivalent to over 4 million Olympic-sized swimming pools, emphasizing its significant presence within the Great Lakes system.
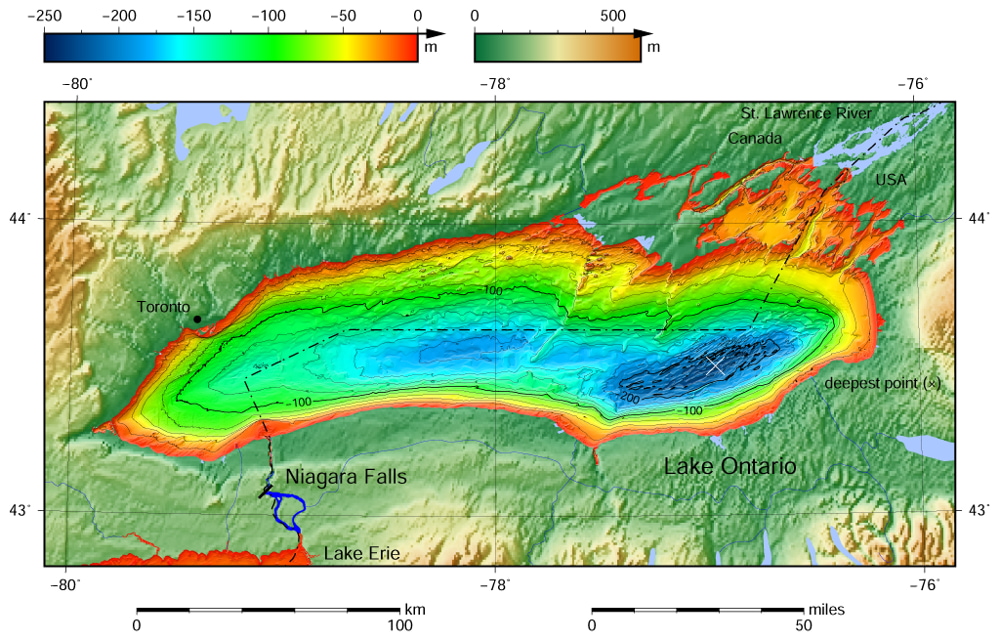
Lake Ontario Depth Map
On average, the depth of Lake Ontario is approximately 86 meters (282 feet). However, there are areas where the lake is much deeper. The maximum depth of Lake Ontario is around 244 meters (802 feet), which can be found near the eastern end of the lake.
To give you an idea of the depth distribution, here are some general ranges:
- Near the shoreline, the lake is relatively shallow, ranging from a few meters to about 15 meters (50 feet).
- As you move further from the shore, the depth gradually increases. You can typically find depths of around 30 to 60 meters (100 to 200 feet) in the mid-lake region.
- In the eastern portion of the lake, near the location of the maximum depth, the water plunges to around 244 meters (802 feet).
Climate
The climate around Lake Ontario is generally warm, with extraordinarily high and low average temperatures throughout the record. However, recent average temperatures are usually higher than in the past due to a warming trend in air temperature in the Lake Ontario basin from 1948 to 2014.
Geography and Hydrology
As one of the Great Lakes, Lake Ontario borders the province of Ontario, Canada, to the north and the state of New York, USA, to the south. Its vast expanse stretches over an area of approximately 7,340 square miles, making it the smallest among its sister lakes. The lake is situated at an elevation of 243 feet above sea level, and its maximum depth reaches an impressive 802 feet. With a shoreline that spans approximately 712 miles, Lake Ontario captivates visitors with its breathtaking beauty and diverse landscapes. From rocky cliffs to sandy beaches, it offers a rich tapestry of scenery that attracts both nature enthusiasts and recreational enthusiasts alike.
Hydrologically, Lake Ontario receives its waters from four primary sources: direct precipitation, inflows from Lake Erie via the Niagara River, runoff from surrounding land, and numerous tributaries. These tributaries, such as the Genesee, Oswego, and Trent Rivers, contribute significant amounts of freshwater to the lake. Lake Ontario drains into the St. Lawrence River, which eventually flows into the Atlantic Ocean. This hydrological connection plays a crucial role in maintaining the lake’s water balance and overall health.
The lake’s hydrology also influences its temperature and water quality. Due to its depth and large volume, Lake Ontario exhibits a thermal stratification pattern, with warmer waters near the surface and cooler waters in the deeper sections. The lake experiences seasonal variations, with warm summers and cold winters shaping its unique climate. Additionally, Lake Ontario supports a diverse ecosystem with various fish species, including lake trout, salmon, and bass, attracting fishing enthusiasts from around the region.
Lake Ontario holds significant importance as a freshwater resource, providing drinking water to millions of people and supporting various industries, such as agriculture and manufacturing, along its shores. Its geographical and hydrological characteristics make it an integral part of the region’s natural and economic landscape, contributing to the overall beauty and vitality of North America’s Great Lakes system.

Comparison with other Great Lakes
When it comes to the Great Lakes, Lake Ontario holds its own unique characteristics, including its depth. Let’s compare Lake Ontario with the other Great Lakes to gain a better understanding of its impressive features.
Lake Ontario, with an average depth of approximately 283 feet (86 meters), stands as the fourth deepest among the Great Lakes. While it may not claim the title of the deepest lake, it still possesses a remarkable depth that captivates the imagination of those who explore its waters.
Let’s take a closer look at the depth comparison among the Great Lakes:
1. Lake Superior: With an average depth of around 483 feet (147 meters), Lake Superior reigns as the deepest and largest of the Great Lakes. It boasts a maximum depth of 1,333 feet (406 meters) near its eastern end.
2. Lake Michigan: As the second largest Great Lake, Lake Michigan reaches an average depth of approximately 279 feet (85 meters). It also showcases a maximum depth of 923 feet (281 meters) near its northern regions.
3. Lake Huron: Lake Huron, the third largest of the Great Lakes, exhibits an average depth of about 195 feet (59 meters). Its deepest point reaches 750 feet (229 meters), making it shallower than both Lake Superior and Lake Michigan.
4. Lake Erie: As the shallowest of the Great Lakes, Lake Erie has an average depth of 62 feet (19 meters). Despite its lesser depth, Lake Erie still presents opportunities for various recreational activities and boasts a maximum depth of 210 feet (64 meters).
Comparing these depths, it becomes clear that Lake Ontario holds a prominent position among its sister lakes. Its average depth surpasses Lake Huron and Lake Erie, showcasing a substantial depth that allows for a diverse range of marine life and recreational pursuits.

Fun Facts
Lake Ontario, one of the Great Lakes, is a geographical marvel and holds intriguing, fun facts. Did you know that Lake Ontario is the 14th largest freshwater lake in the world by surface area? It spans an impressive 7,340 square miles, making it a vast expanse to explore.
Furthermore, the lake’s depth is noteworthy, reaching a maximum of 802 feet. Another fascinating fact is that Lake Ontario is known for its mesmerizing sunsets. The combination of its size, the surrounding landscapes, and atmospheric conditions creates a captivating display of colors as the sun dips below the horizon.
Additionally, Lake Ontario is home to various fish species, making it a popular destination for fishing enthusiasts. Anglers can try their luck catching lake trout, salmon, bass, and more, contributing to the region’s vibrant recreational activities.
Lastly, the lake’s diverse shoreline offers picturesque beaches, rocky cliffs, and charming coastal towns, providing endless opportunities for relaxation and exploration.
Settlements and Activities on the Lake
European settlements have been documented on the lake since the early 1600s. The lake was the border between the Huron and their vassals and the Iroquois Confederacy in pre-European times. After the French and Indian War, forts on the U.S. side of the lake became American. European settlement began during the American Revolution. After the War of 1812, the lake became the center of a thriving business district.
There are over 30 000 islands in Lake Ontario, most of which are uninhabited. Some of these islands are home to significant bird populations, such as the gull colony on Toronto Island. The lake also provides drinking water for millions of people in Ontario and New York State.

Conclusion
In conclusion, Lake Ontario is a treasure worth cherishing. Its depth, beauty, and ecological importance make it a valuable asset to both nature and humanity. As stewards of the environment, it is our responsibility to protect and preserve this remarkable lake for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
FAQs
Where is Lake Ontario’s deepest point?
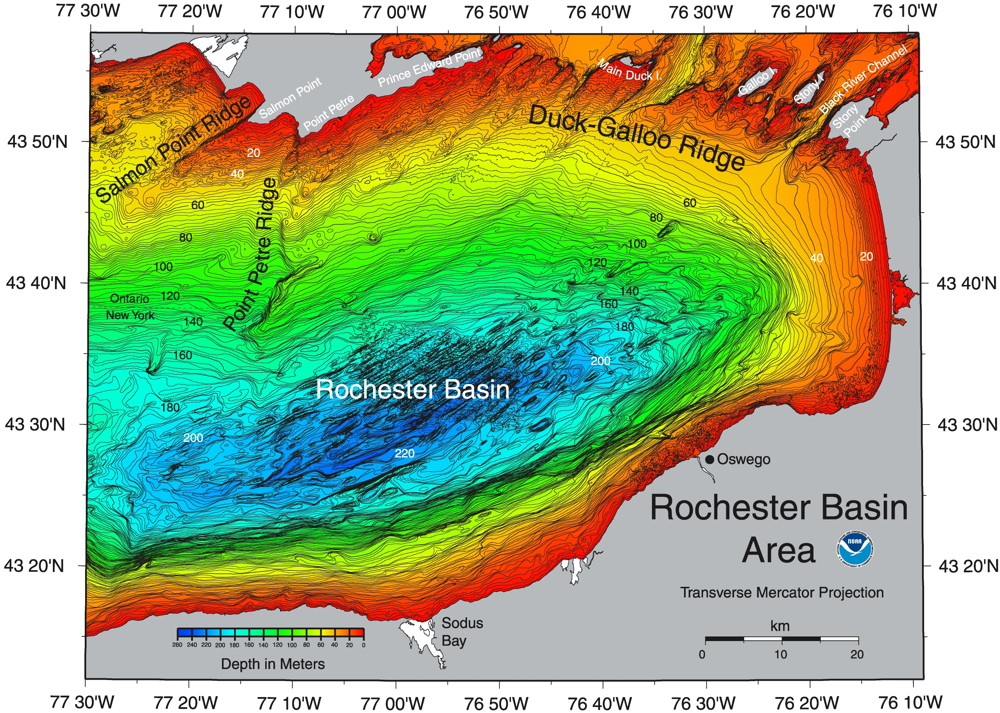
The deepest point in Lake Ontario is Rochester Basin. It is located in the southeast corner of Lake Ontario and is approximately 802 feet (244 m) deep. The deepest point in Lake Ontario, Rochester Basin, is located just south of the city of Rochester.
Is Lake Ontario safe for swimming?
Lake Ontario is a freshwater lake, which means it’s safe for swimming. The water in Lake Ontario is not salty like ocean water, so no sharks or other dangerous creatures live in it. Swimming in Lake Ontario is a great way to cool off in the summer and take a refreshing swim in the winter.
Does Lake Ontario have RIP current?
RIP currents are solid and often unexpected flows of water that pull you away from the shore. They are usually created by natural causes, such as the effect of waves crashing on a beach (the breaking waves push water away from shore) or tidal currents. They can be deadly if they sweep you out to sea or up against a rocky coast.
Lake Ontario does not have RIP currents. The shape of the lake, with its narrows at the Niagara River and wide mouth at Lake Erie, helps keep water moving slowly in a circle. The gentle flow stops ripping currents from forming. RIP currents are standard on the Atlantic coast and the Gulf of Mexico.

