The Great Lakes contain over 20% of the world’s fresh water and are so important that in 1973 they were designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
But how were these large bodies formed?
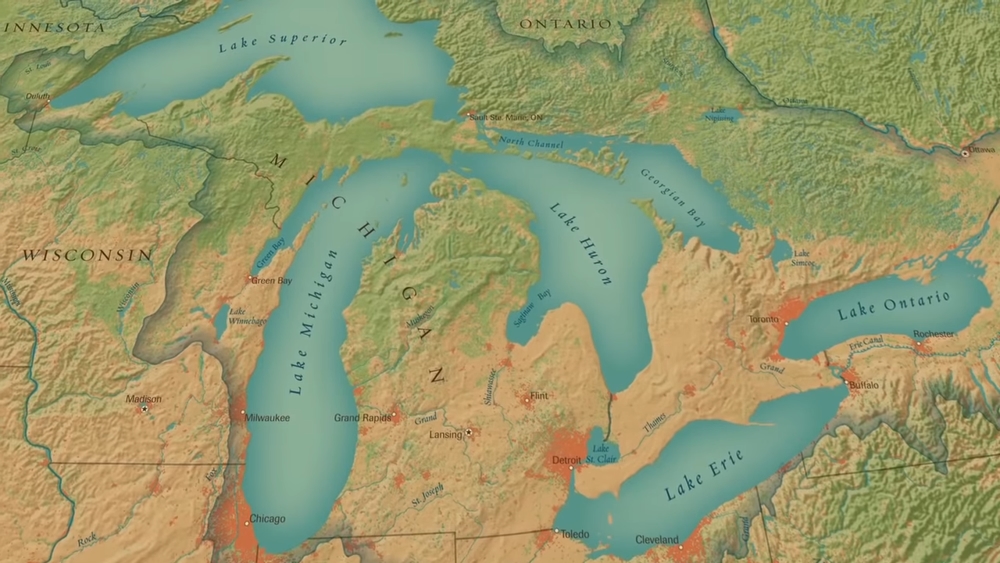
The Great Lakes are a series of freshwater lakes in Canada and the United States. The largest lake is Lake Superior, which has an area of 31,700 square kilometers (12,100 sq mi). The total surface area of the Great Lakes is over 96,000 square kilometers (37,000 sq mi), making them larger than the state of South Carolina or Belgium.
The lakes were formed at the end of the last Ice Age when retreating glaciers left behind large deposits of sand and gravel. The lakes are very deep in places—Lake Michigan is 1,300 feet (400 m) deep—and the bottoms of some lakes lie more than 600 feet (200 m) below sea level.
How are lakes typically formed?
1) Glacial activity: This is the most common way lakes are formed in the Northern Hemisphere. When a glacier moves, it scrapes away at the land beneath it. This can create depressions in the land that fill with water to form lakes.
2) Volcanic activity: Volcanoes can also create lakes by forming crater lakes. Crater lakes form when a volcano erupts, and the resulting crater fills with water.
3) Fluvial activity: Fluvial activity is another way lakes can be formed, typically in areas with a lot of rainfall. When rivers or streams overflow their banks, they can create depressions in the land that fill with water to form lakes.
What are the Great Lakes?
Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. They are the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth and hold over 20% of the world’s fresh water. The Great Lakes are a vital source of drinking water for millions of people and play an essential role in the region’s economy.
Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes and covers nearly 31,700 square miles in area. It has a maximum width of about 53 miles and an average depth of 279 feet. Lake Superior contains the highest amount of water found in the Great Lakes, with just over two quadrillion gallons.
Lake Superior is known for its cold temperatures and strong winds. It freezes completely during winters, with average ice coverage lasting from November to April.
Lake Superior is the cleanest of all the Great Lakes, with only two percent of its water being polluted. It is also considered the clearest due to its depths and current.
Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes in terms of surface area, volume, water level elevation, and shoreline length. It contains more than 3,000 islands that are within the U.S. and Canada, with Isle Royale being the largest at 45 miles long and over 14 miles wide.

Huron Lake
Huron Lake is the second largest of the five Great Lakes. It covers an area of 23,000 square miles and has a maximum depth of 274 feet. The Huron River on one side and the Detroit River on the other divide Huron Lake into two unequal parts.
The northern part of Huron Lake is called Georgian Bay, and it contains a number of smaller lakes, including Lake Simcoe, which is the third largest lake in Ontario.

Michigan Lake
Michigan Lake is the third largest of the Great Lakes and has a surface area of 22,300 square miles. The lake is bordered by 22 counties in Michigan, known as “the thumb region,” as well as Ontario, Canada.
Michigan Lake’s depth ranges from 325 feet to 950 feet deep, with an average of 340 feet deep. The maximum water level is 577 ft above sea level, and the minimum is 577 ft below sea level.
The lake has a shoreline of 2,827 miles long. The average depth of Michigan Lake is 62 feet deep. The St. Marys River feeds the lake and drains into Lake Huron through the Detroit River.
Michigan Lake has a maximum depth of 955 feet, making it the second deepest lake in the United States. (Crater Lake, Oregon, is the deepest at 1,949 feet.) Lake Michigan is home to more than 3,000 fish and other aquatic life species. The lake is also home to many species of birds, including the bald eagle.

Erie Lake
Erie Lake is the 4th largest of the Great Lakes. It is located in the state of Pennsylvania and lies on the border between New York and Ohio. Erie Lake has no islands but does have a few peninsulas. The lake also has many bays and harbors.
Erie Lake is connected to Lake Huron by the St. Mary’s River, which flows through a channel called the Sault Ste Marie Channel. The lake was named after the Erie Tribe of Native Americans that lived in this area.
The lake has an average depth of 62 feet and a maximum depth of 210 feet. The lake is also home to many fish species, including walleye, yellow perch, white bass, and salmon. The lake is also home to many types of waterfowl.

Ontario Lake
Lake Ontario is the smallest of the great lakes in terms of surface area, but it is the 14th largest lake in the world.
The smallest of the Great Lakes, Lake Ontario, covers an area of 7,540 square miles (19,930 sq km). It is the smallest of the five Great Lakes by volume, containing 2,941 cubic miles (12,070 cubic km) of water.
Lake Ontario is bounded on its north and northeast shores by the Canadian province of Ontario. The Niagara River, which flows northward from Lake Erie, forms the boundary between Ontario and New York.
The lake is divided by a narrow strait called the Niagara Escarpment that runs from the Niagara River in the north to Hamilton, Ontario, in the south. The city of Toronto sits at the western end of Lake Ontario.
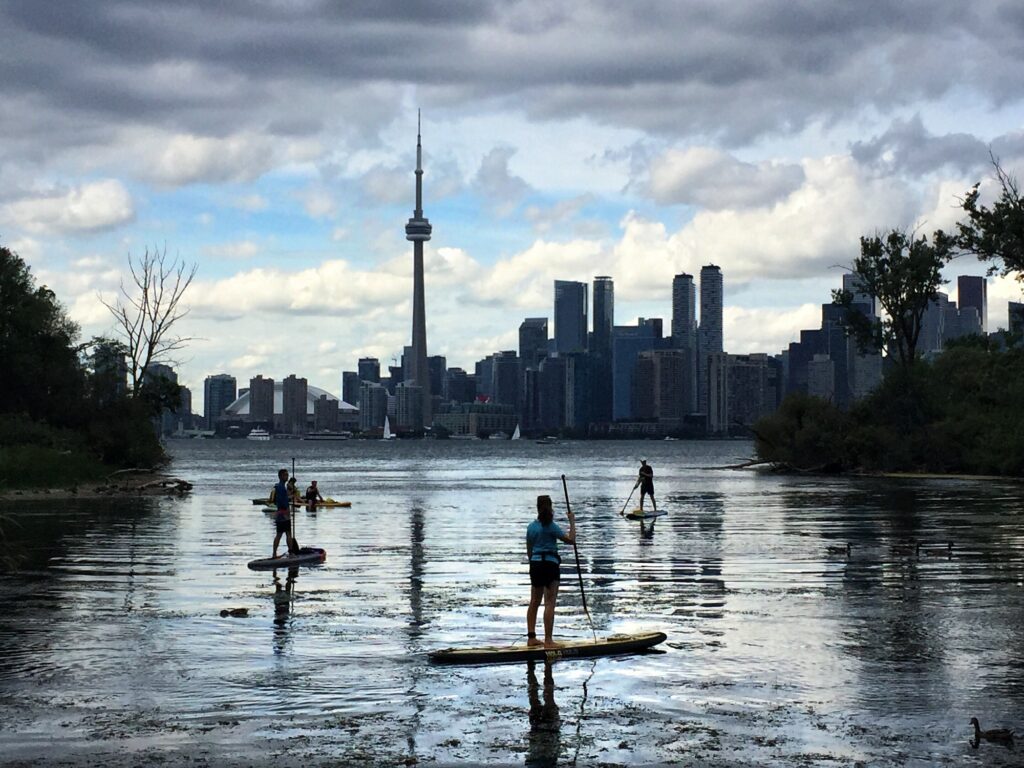

Why are the great lakes important?
The Great Lakes are important for several reasons. They provide drinking water to millions of people and water for irrigation of crops. They also provide recreation for millions of people each year, including swimming, boating, and fishing.
The Great Lakes are the largest freshwater system in the world. They contain about 20 percent of the world’s supply of surface freshwater. The Great Lakes are so large they have their own weather systems!
How long ago were the Great Lakes formed?
The Great Lakes formed around 14,000 years ago as the last ice age ended. As the glaciers melted, water filled in depressions left behind by the ice sheet and began to form lakes.
Which great lake is the deepest?
Lake Superior is the deepest of the Great Lakes, with an average depth of 1 332 feet (406 m). It is 307 miles (494 km) long by 118 miles (190 km) wide with a shoreline of 1,827 miles (2,938 km). It is the largest by volume (1 605 cubic miles or 11 565 km3) and the third-largest by surface area (7 030 square miles or 18 948 km2). Lake Superior drains 31,700 square miles (82,100 km2) into Lake Huron via the St. Marys River and the Soo Locks; it has an average discharge of 1 025 cubic feet per second (31 m3/s).
Why are the great lakes not salty?
The Great Lakes were formed by the glaciers during the ice age and are freshwater because they are not connected to the ocean. The great lakes are fed by rivers which in turn are fed by rainwater. The water flowing into the great lakes carries away the low concentrations of minerals in the water. This process keeps the great lakes from being salty.

